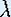 x
(1 - x)
x
(1 - x)
One-Dimensional Dynamical Systems
Part 3: Iteration
The function
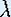 x
(1 - x)
x
(1 - x)
is known as the Logistic map. The Logistic map depends on the
parameter 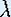 . As we
already saw in the
Introduction, the
dynamics of the map depends on this parameter. However, the difference
in the dynamics is not qualitatively significant for every different
. As we
already saw in the
Introduction, the
dynamics of the map depends on this parameter. However, the difference
in the dynamics is not qualitatively significant for every different
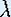 . In dynamical
systems theory, we like to think of the whole set of maps depending on
. In dynamical
systems theory, we like to think of the whole set of maps depending on
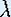 as one
object. To express this idea, we speak of the one-parameter Logistic
family. We discuss the dynamics of such a family by
showing the qualitatively different types of possible dynamics, and by
showing in which intervals of the parameter space these dynamics
occur. The one-parameter Logistic family is our object of study.
as one
object. To express this idea, we speak of the one-parameter Logistic
family. We discuss the dynamics of such a family by
showing the qualitatively different types of possible dynamics, and by
showing in which intervals of the parameter space these dynamics
occur. The one-parameter Logistic family is our object of study.
The dependency on
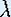 and x
is nicely illustrated by the Java Applet
Iteration of the Logistic Map of Andy Burbanks. Use this applet to
study how the graph of the map changes as you increase
and x
is nicely illustrated by the Java Applet
Iteration of the Logistic Map of Andy Burbanks. Use this applet to
study how the graph of the map changes as you increase
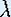 , and what
happens with the orbit of the chosen initial point. For fixed
, and what
happens with the orbit of the chosen initial point. For fixed
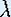 do the orbits
of all the points in the interval [0,1] behave the same?
do the orbits
of all the points in the interval [0,1] behave the same?
![[HOME]](/pix/home.gif) The Geometry Center Home Page
The Geometry Center Home Page
Written by Hinke Osinga
Comments to:
webmaster@geom.umn.edu
Created: Apr 1 1998 ---
Last modified: Wed Apr 8 18:44:56 1998