The Fixed Point Theorem
- Theorem:
- Let f be a continuous function on
[0,1] so that f(x) is in [0,1] for all x in [0,1]. Then there
exists a point p in [0,1] such that f(p) = p, and p is called a
fixed point for f.
- Proof:
- If f(0) = 0 or f(1) = 1 we are done
 .
So assume the points 0 and 1 are not fixed points. Let
g(x) = f(x) -x. Then since 0 and 1 are not fixed points
g(0) = a > 0 and g(1) = b < 0
.
So assume the points 0 and 1 are not fixed points. Let
g(x) = f(x) -x. Then since 0 and 1 are not fixed points
g(0) = a > 0 and g(1) = b < 0
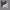 . So by the
Intermediate Value Theorem, there exists a point p
so that g(p) = 0
. So by the
Intermediate Value Theorem, there exists a point p
so that g(p) = 0 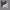 .
The point p is a fixed point for f
.
The point p is a fixed point for f
 .
.
Introductory Page
 .
So assume the points 0 and 1 are not fixed points. Let
g(x) = f(x) -x. Then since 0 and 1 are not fixed points
g(0) = a > 0 and g(1) = b < 0
.
So assume the points 0 and 1 are not fixed points. Let
g(x) = f(x) -x. Then since 0 and 1 are not fixed points
g(0) = a > 0 and g(1) = b < 0
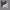 . So by the
Intermediate Value Theorem, there exists a point p
so that g(p) = 0
. So by the
Intermediate Value Theorem, there exists a point p
so that g(p) = 0 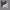 .
The point p is a fixed point for f
.
The point p is a fixed point for f
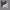 .
.