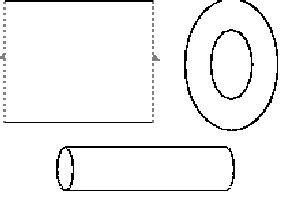
Each of the above is an annulus: a gluing diagram of an annulus,
a ring, and a tube.

The above box has one boundary that runs along all four sides.
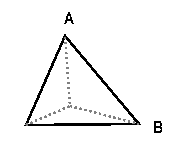
In the above picture, segment AB is an edge of the tetrahedron.
The above segment is finite. It does not extend forever in any direction.
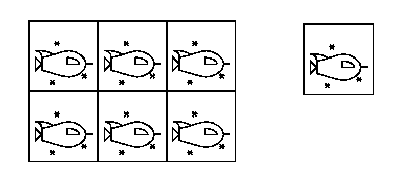
In the above picture, the small square on the right with its contents is the fundamental doman for the tiling on the left.
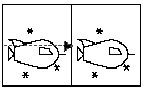
The square on the left is the orignal square, called the preimage. The image to its right is formed by moving the preimage in the direction of the arrow. The total distance which the image is moved is equal to the length of the arrow. Note that the arrow is there for demonstrative purposes only; it is not part of the preimage.
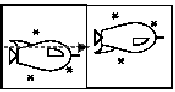
Here, the preimage on the left is first reflected across the arrow and then a glide is applied to it (see glide), giving the image to the right.
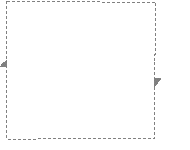
This is a gluing diagram of a Mobius strip. If one were to cut it out,stretch it, and glue the sides together so that the arrows lined up, it would look like the representation of a Mobius strip in three dimensional space. This Mobius strip diagram has the same intrinsic topology of a Mobis strip placed in three dimensional space.
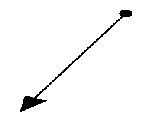
The ray is infinite in the direction of the arrow.
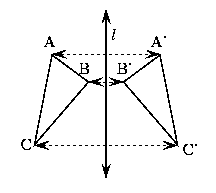
Triangle ABC is reflected about line l to make triangle A'B'C'.
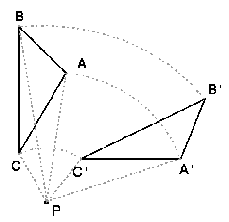
Triangle ABC is rotated (45 degrees) about point P to make triangle A'B'C'
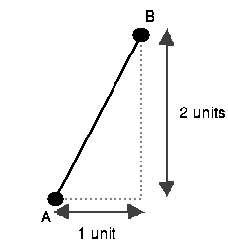
Segment AB extends up two units for every unit to the right that it extends. Thus, it has slope 2/1.
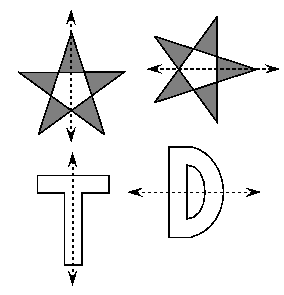
Each of the above shapes is symmetrical since the part of the shape on one side of the arrow is the same as the part of the shape on the other side of the arrow except for its position.

Above is a doughnut-shaped torus and a torus gluing diagram. They are both intrinsically topologically a torus.


The above rotation and reflection are examples of transformations